Multimodal detection of protein isoforms and nucleic acids from low starting cell numbers
Abstract
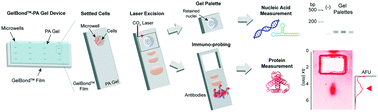
Protein isoforms play a key role in disease progression and arise from mechanisms involving multiple molecular subtypes, including DNA, mRNA and protein. Recently introduced multimodal assays successfully link genomes and transcriptomes to protein expression landscapes. However, the specificity of the protein measurement relies on antibodies alone, leading to major challenges when measuring different isoforms of the same protein. Here we utilize microfluidic design to perform same-cell profiling of DNA, mRNA and protein isoforms (triBlot) on low starting cell numbers (1–100 s of cells). After fractionation lysis, cytoplasmic proteins are resolved by molecular mass during polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE), adding a degree of specificity to the protein measurement, while nuclei are excised from the device in sections termed “gel pallets” for subsequent off-chip nucleic acid analysis. By assaying TurboGFP-transduced glioblastoma cells, we observe a strong correlation between protein expression prior to lysis and immunoprobed protein. We measure both mRNA and DNA from retrieved nuclei, and find that mRNA levels correlate with protein abundance in TurboGFP-expressing cells. Furthermore, we detect the presence of TurboGFP isoforms differing by an estimated <1 kDa in molecular mass, demonstrating the ability to discern different proteoforms with the same antibody probe. By directly relating nucleic acid modifications to protein isoform expression in 1–100 s of cells, the triBlot assay holds potential as a screening tool for novel biomarkers in diseases driven by protein isoform expression.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...