Multivariate analysis of PIXE + XRF and PIXE spectral images
Abstract
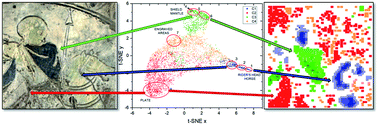
In this work, we demonstrate the usefulness of multivariate techniques for the analysis of two-dimensional (2D) spectral images obtained by proton beam ionization (PIXE mode) and combined proton beam and photoionization with an X-ray tube (PIXE + XRF mode). Two different multivariate analysis approaches were used: (i) principal component analysis (PCA) for dimensionality reduction followed by k-means clustering for the identification of different sample regions and (ii) t-distributed stochastic neighbour embedding technique (t-SNE). In PCA + k-means clustering, similar pixels were grouped into different clusters where a direct connection between individual clusters and elements identified from cluster spectra resulted in the fast image segmentation and identification of different sample regions. t-SNE was used for dimensionality reduction and simple 2D visualization of high dimensional data. Three different cases were investigated: (i) qualitative analysis of 2D spectral maps having pixel spectra with a high number of counts per pixel in the full range of measured X-ray energies collected in PIXE + XRF mode excitation, (ii) qualitative and semi-quantitative analysis of 2D spectral maps having pixel spectra with medium to low counts per pixel collected in PIXE mode, and (iii) qualitative and quantitative analysis of 2D spectral maps having medium to low statistics per pixel obtained in PIXE mode. In the actual case studies, we identified all the pigments in artificial and real samples, namely, illumination from a historical book, and quantitatively characterized the identified gold layer and Niello decoration on an archaeological plate of Roman origin. In the last example, we were able to identify the sample regions with similar layer thicknesses and obtain the layer thickness and elemental concentrations. We demonstrated that high statistics spectra that would contain enough information for qualitative and/or quantitative analysis of major, minor and even trace elements can be deduced using multivariate analysis methods even from low-statistics individual pixel spectra collected during 2D scanning of objects under investigation. This could be of particular importance for sensitive samples that could be damaged during long irradiation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...