Abstract
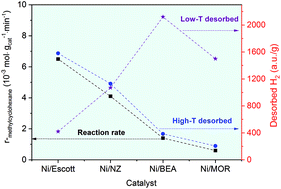
Natural and synthetic (BEA, MOR) zeolite-supported nickel (∼5 wt%) catalysts were prepared and employed for the hydrogenation of toluene and hydrodeoxygenation of anisole in a continuous-flow reactor. Ni/BEA and Ni/MOR display a higher level of metal dispersion and stronger metal–support interaction compared to the Ni/NZ and Ni/Escott catalysts, resulting in a higher concentration of charge-compensating Ni species and a larger high-temperature reduction peak. The Ni/BEA and Ni/MOR also present a significant mass of low-temperature desorbed H2 (centred at 150 °C) based on H2-TPD, suggesting the H species are weakly adsorbed on small Ni clusters. In contrast, the H species were strongly adsorbed by the bulk Ni crystal over Ni/Escott and Ni/NZ, which were desorbed at maxima between 211 and 222 °C. We propose that the strongly adsorbed H species play a crucial role in the hydrogenation of toluene, leading to a significantly higher yield of methylcyclohexane over Ni/Escott and Ni/NZ compared to Ni/BEA and Ni/MOR. Both metal and acid sites are required in the hydrodeoxygenation of anisole. The strong Brønsted acid sites and numerous smaller Ni species over Ni/BEA facilitated the transalkylation of anisole to phenol and methylanisole and subsequently hydrogenolysis of phenol to benzene, followed by the hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexane.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 Green Chemistry Hot Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...