Rapid biosynthesis of phenolic glycosides and their derivatives from biomass-derived hydroxycinnamates†
Abstract
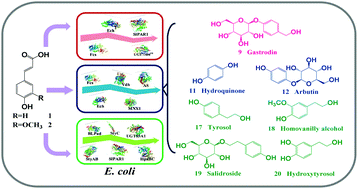
Biomass-derived hydroxycinnamates (mainly including p-coumaric acid and ferulic acid), which are natural sources of aromatic compounds, are highly underutilized resources. There is a need to upgrade them to make them economically feasible. Value-added phenolic glycosides and their derivatives, both belonging to a class of plant aromatic natural products, are widely used in the nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. However, their complex aromatic structures make their efficient biosynthesis a challenging process. To overcome this issue, we created three novel synthetic cascades for the biosynthesis of phenolic glycosides (gastrodin, arbutin, and salidroside) and their derivatives (hydroquinone, tyrosol, hydroxytyrosol, and homovanillyl alcohol) from p-coumaric acid and ferulic acid. Moreover, because the biomass-derived hydroxycinnamates directly provided aromatic units, the cascades enabled efficient biosynthesis. We achieved substantially high production rates (up to or above 100-fold enhancement) relative to the glucose-based biosynthesis. Given the ubiquity of the aromatic structure in natural products, the use of biomass-derived aromatics should facilitate the rapid biosynthesis of numerous aromatic natural products.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...