The metabolic regulation of Fuzhuan brick tea in high-fat diet-induced obese mice and the potential contribution of gut microbiota†
Abstract
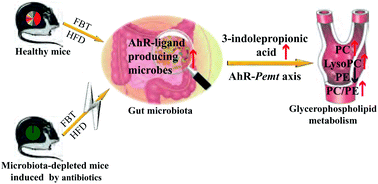
This study investigated the metabolic effects of Fuzhuan brick tea (FBT) in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese mice and the potential contribution of gut microbiota. The results showed that FBT ameliorated the HFD-induced glycerophospholipid metabolic aberrance, specifically increased the serum levels of phosphatidylcholines (PCs), lysophosphatidylcholines (LysoPCs), and the ratio of PC to phosphatidylethanolamines (PE). Besides, FBT increased the serum level of gut microbiota-derived aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) ligand, 3-indole propionic acid, as well as the relative abundance of intestinal AhR-ligand producing bacteria such as Clostridiaceae, Bacteroidales_S24-7_group, and Lactobacillaceae. However, the metabolic benefits of FBT were weakened when the gut microbiota were depleted by antibiotic treatment, thereby suggesting that gut microbiota was required for FBT to regulate glycerophospholipid metabolism. Indeed, the metabolites regulated by FBT were significantly correlated with the AhR-ligand producing bacteria. The KEGG pathway enrichment analysis and expressions of AhR target genes indicated that FBT would improve the glycerophospholipid metabolism via the AhR-Pemt signal axis, in which the gut microbiota and their metabolites played pivotal mediators. Overall, FBT could be a functional beverage to improve HFD-induced metabolic disorders in a gut microbiota dependent manner.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...