Anti-inflammatory effects of oleic acid and the anthocyanin keracyanin alone and in combination: effects on monocyte and macrophage responses and the NF-κB pathway†
Abstract
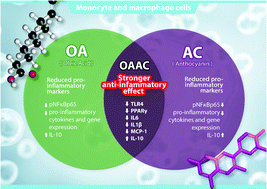
Monocyte recruitment and activation of macrophages are essential for homeostasis but are also related to the development and progression of cardiometabolic diseases. The management of inflammation with dietary components has been widely investigated. Two components that may influence inflammation are unsaturated fatty acids such as oleic acid (OA; 18:1cis-9) and antioxidant compounds like anthocyanins. Molecular and metabolic effects of such bioactive compounds are usually investigated in isolation, whereas they may be present in combination in foods or the diet. Considering this, we aimed to analyze the effects of OA and the anthocyanin keracyanin (AC) alone and in combination on toll-like receptor-mediated inflammatory responses in monocytes and macrophages. For this, THP-1-derived macrophages and monocytes were exposed to 3 treatments: OA, AC, or the combination (OAAC) and then stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Inflammation-related gene expression and protein concentrations of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, MCP-1, and IL-10 were assessed. Also, NFκBp65, IκBα, and PPAR-γ protein expression were determined. OA, AC, and OAAC decreased pNFκBp65, PPARγ, IκBα, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and MCP-1 and increased IL-10. MCP-1 protein expression was lower with OAAC than with either OA and AC alone. Compared to control, OAAC decreased mRNA for TLR4, IκKα, IκBα, NFκB1, MCP-1, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β more than OA or AC did alone. Also, IL-10 mRNA was increased by OAAC compared with control, OA, and AC. In summary, OA and AC have anti-inflammatory effects individually but their combination (OAAC) exerts a greater effect.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...