Artichoke leaf extract supplementation lowers hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation and increases multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 in mice fed a high-fat and high-cholesterol diet
Abstract
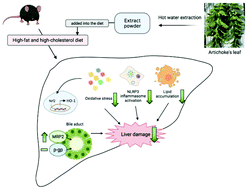
Artichoke (Cynara scolymus) leaf extract (ALE) contains many phytonutrients that may have antioxidant and anti-inflammation activities against many diseases including liver damage. To investigate the protective effects of ALE on high-fat and high-cholesterol (HFHC) diet-induced steatohepatitis and liver damage in mice, twenty-four female mice were fed an HFHC diet without or with 0.5% and 1% ALE supplementation for 6 weeks. The antioxidant and anti-inflammation activities and histological changes in the liver after ALE treatment were evaluated. The results show that ALE treatment reduced the HFHC diet-induced elevation of liver damage, as indicated by an increased alanine aminotransferase activity in plasma and perivenular inflammatory infiltrates in the liver. In addition, ALE ameliorated HFHC diet-induced depletion of hepatic glutathione (GSH) and elevations of plasma total cholesterol, triglyceride and hepatic triglyceride. ALE suppressed HFHC diet-induced accumulation of cholesterol precursors, including squalene and desmosterol in the liver. Higher hepatic GSH contents and activities of GSH-related enzymes were observed after ALE treatment. Higher expressions of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) were induced by the HFHC diet; however, ALE treatment reduced HO-1 expression. The NOD-like receptor protein 3, caspase-1, and interleukin-1β protein and mRNA levels were reduced in the liver by ALE. A higher multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 expression in the liver was found after ALE treatment. These results suggest that ALE may ameliorate oxidative stress, inflammation and lipid metabolism disorder in HFHC diet-induced steatohepatitis and liver damage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...