A polysaccharide from natural Cordyceps sinensis regulates the intestinal immunity and gut microbiota in mice with cyclophosphamide-induced intestinal injury
Abstract
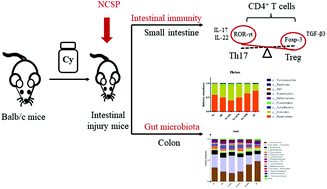
A polysaccharide from Cordyceps sinensis (NCSP) was reported to attenuate intestinal injury and regulate the balance of T helper (Th)1/Th2 cells in immunosuppressed mice. However, whether it influences Th17 and regulatory T (Treg) cells as well as gut ecology remains unknown. In the present study, the intestinal injury mouse model was also established by intraperitoneal injection of cyclophosphamide (Cy) for three consecutive days. NCSP was found to increase the number of CD4+ T cells, stimulate the secretion of interleukins (IL)-17 and IL-21, and the expression of transcription factor (retinoic acid-related orphan receptor (ROR)-γt). The levels of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β3 and transcription factor (forkhead box (Fox)p-3) were increased in NCSP-treated groups. Moreover, NCSP upregulated the mRNA expression of toll like receptors (TLR-2, -6 and -9), while it downregulated the TLR-4 expression. In addition, NCSP modulated the intestinal microbiota composition and increased the levels of SCFAs. These findings indicated that NCSP may enhance intestinal immunity and have the potential to become a prebiotic to regulate intestinal microbiota.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...