Lactobacillus paracasei modulates the gut microbiota and improves inflammation in type 2 diabetic rats
Abstract
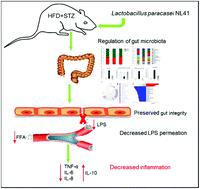
This study aimed to investigate the effects of probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei NL41 on inflammation and the gut microbiota of type 2 diabetic (T2D) rats induced by high-fat diet (HFD) and low-dose streptozotocin (STZ). A T2D rat model was established by inducing Sprague-Dawley rats with HFD/STZ, followed by 12-weeks L. paracasei NL41 gavage. The blood, colonic tissues, and feces samples of these rats were collected for inflammation, histology, and intestinal microbiota profiling. L. paracasei NL41 treatment induced remarkable improvement in the inflammatory status by decreasing the levels of serum lipopolysaccharides (LPS), free fatty acids (FFA), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-8 and increasing the level of IL-10. Gut barrier function was significantly protected in NL41-treated rats. Moreover, the strain NL41 induced changes in the microbiota structure and influenced the relative abundance of the key species. Specifically, Bacteroides, Clostridia (specifically, Ruminococcus torques), and Parasutterella were significantly reduced, while some beneficial microorganisms (Bacteroidales_S24-7_group and the families Lachnospiraceae and Ruminococcaceae) were enriched by NL41. The correlational analyses indicated that L. paracasei NL41 ameliorating inflammation was closely related to the key species of the gut microbiota. The present study indicates that probiotic L. paracasei NL41 decreases LPS-induced inflammation by improving the gut microbiota and preserving intestinal integrity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...