Tetrahydrocurcumin alleviates allergic airway inflammation in asthmatic mice by modulating the gut microbiota†
Abstract
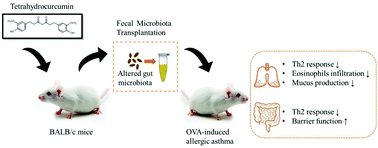
Dietary factors can reshape the gut microbiota and consequently affect disease progression. We previously reported that tetrahydrocurcumin (THC), the major active metabolite of curcumin (Cur), could ameliorate allergic inflammation in asthmatic mice. Herein, we aimed to investigate whether THC or Cur exerts anti-inflammatory effects on allergic asthma via modulating gut microbiota. Ovalbumin (OVA)-induced asthmatic mice were treated with Cur or THC, and the gut microbiota profiles were analyzed by 16S rRNA sequencing. Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) from Cur- or THC-fed donor mice was administered to OVA-induced asthmatic mice. Nasal symptoms and inflammation patterns of lungs and colons were evaluated in control, OVA-induced and Cur-or THC-treated mice. Both Cur and THC treatment could alter the compositions of the gut microbiota in asthmatic mice, characterized by a significant decrease in the ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes; Cur or THC supplementation also reduced the relative abundances of pro-inflammatory bacteria, e.g., Proteobacteria, Intestinimonas, Unidentified-Ruminococcaceae, and Lachnospiraceae, in OVA-induced mice. The relative abundances of Unidentified-Ruminococcaceae, Romboutsia, Intestinimonas, Akkermansia, and Mucispirillum were positively associated with the levels of Th2-related factors in asthmatic mice upon Cur or THC treatment. Moreover, THC-FMT showed better preventive effects than Cur-FMT on the development of allergic inflammation in OVA-induced mice, resulting in a reduction in symptoms and Th2-mediated inflammation in both lung and colon tissues. The results reveal that Cur- or THC-mediated alleviation of airway allergic inflammation is dependent on gut microbiota modulation. THC-induced gut microbiota may have therapeutic potential for asthma treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...