Olive oil cake extract stabilizes the physiological condition of lipopolysaccharide-challenged piglets by reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory responses and modulating the ileal microbiome
Abstract
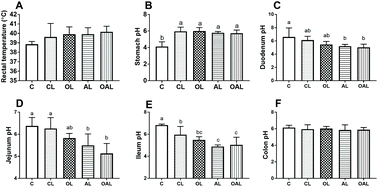
Olives are a rich source of compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. This study was designed to investigate whether a standardized olive cake extract was able to alleviate oxidative stress, inflammation and intestinal villus damage in a model of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-challenged piglets. Thirty weaned piglets (6.9 ± 0.9 kg) were assigned to five groups using a randomized complete block design. Piglets were fed a basal diet before intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of physiological saline (C); fed a basal diet alone (CL) or fed a basal diet plus an olive cake extract (OL), antibiotics (AL), or olive cake extract plus antibiotics (OAL) before i.p. injection of LPS. The feeding period lasted for 2 weeks. Piglets were euthanized 4 h after the LPS injection. Systemic oxidative and inflammatory status and intestinal morphology were evaluated. LPS challenge significantly lowered the serum levels of GSH-Px, SOD and ALB and increased the serum concentration of MDA, NO, LDH, ALT, AST, TNF-α, IL-6, DAO and D-xylose (P < 0.05), as extracted from the comparison of piglets in the C and CL groups. Intestinal morphology was altered in the duodenum and ileum, displaying that the CL group had significantly lower villus height (VH), higher crypt depth (CD) and lower VH/CD compared with the control group (P < 0.05). Moreover, feed supplementation was able to partially mitigate the negative effects of LPS challenge in all groups (OL, AL, and OAL), as evidenced by the significantly increased serum levels of GSH-Px, SOD, ALB and IL-10 and decreased concentration of MDA, NO, LDH, ALT, AST, TNF-α, IL-6, DAO and D-xylose, compared with the CL group (P < 0.05). Alterations in intestinal morphology were also prevented and the OL, AL, and OAL groups had significantly lower CD and higher VH/CD compared with the CL group (P < 0.05), both in the ileum and duodenum. Furthermore, the positive effect in the relative abundance of intestinal Lactobacillus and Clostridium at the genus level was also observed for the OL group compared to the CL group. In summary, dietary supplementation with an olive cake extract stabilized the physiological condition of piglets subjected to an acute LPS challenge by reducing oxidative stress and the inflammatory status, improving intestinal morphology and increasing the abundance of beneficial intestinal bacteria. This trial was registered at Zhejiang University (http://www.lac.zju.edu.cn) as No. ZJU20170529.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...