l-Arabinose suppresses gluconeogenesis through modulating AMP-activated protein kinase in metabolic disorder mice†
Abstract
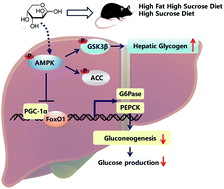
L-Arabinose is a kind of plant-specific five-carbon aldose with benefits in type 2 diabetes mellitus. It has been shown to have good properties in improving glucose homeostasis, but the underlying molecular mechanisms are still not clear. Hepatic gluconeogenesis is critical for regulating glucose homeostasis. Here, this study aimed to investigate whether L-arabinose could improve glucose metabolism via suppressing hepatic gluconeogenesis. High-fat–high-sucrose diet (HFHSD) or high-sucrose diet (HSD)-fed mice were supplemented with or without L-arabinose for 12 weeks. Fasting blood glucose levels were measured and glucose tolerance test and the histological analysis were performed after L-arabinose administration. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α (PGC1α), Forkhead box O1 (FoxO1), phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) expression levels were determined by RT-PCR and western blotting. As expected, L-arabinose apparently decreased body weight and attenuated hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance caused by HFHSD or HSD. L-Arabinose also had beneficial effects on glycogen synthesis by inactivating GSK3β. The expression levels of gluconeogenic genes were all decreased by L-arabinose administration in vivo and in vitro. In addition, our work revealed that AMPK is required for the inhibitory effects of L-arabinose on hepatic gluconeogenesis. L-Arabinose significantly up-regulated the phosphorylated levels of AMPK and its downstream protein ACC. Furthermore, blocking AMPK signaling through an inhibitor (compound C) or siAMPK significantly attenuated the inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis and the promotion of glycogen synthesis with L-arabinose, indicating that the inhibitory effect of L-arabinose on hepatic gluconeogenesis was AMPK dependent. Our work revealed that L-arabinose is a promising natural product for the regulation of hyperglycemia through inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis by activating AMPK.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...