Impact of sodium silicate on lead release from lead(ii) carbonate†
Abstract
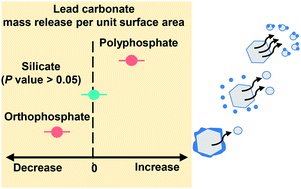
Silicates have been added to drinking water for decades, mainly to control colour by dispersing oxidized iron and manganese. Silicates have been used occasionally to control lead release, but there is no consensus on whether they are effective. Moreover, there are concerns that silicates may disperse particulate lead. We evaluated the effect of sodium silicate on lead release from a model lead(II) carbonate powder using a continuous-flow stirred-tank reactor. We tested a wide range of pH and dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) concentrations (pH 7.5 or 9, and 5 or 50 mg C per L). We compared sodium silicate against an inhibitor-free control, a better-characterized inhibitor (orthophosphate), and a widely used sequestrant (polyphosphate). Sodium silicate did not have a statistically significant impact on lead release at pH 7.5, regardless of the DIC concentration. At pH 9 it accompanied 80% more lead release at 5 mg C per L and 21% less lead release at 50 mg C per L, compared with controls at matched pH and DIC settings. Sodium silicate did not influence the crystalline phase composition, but it did adsorb to lead(II) carbonate. This may account for its effects at pH 9. Orthophosphate was the more effective inhibitor, yielding 33–96% less lead release than matched controls. Orthophosphate inhibition was attributed to conversion from lead(II) carbonate to hydroxylpyromorphite (Pb5(PO4)3OH) and adsorption to lead(II) carbonate in the absence of a phase conversion (i.e., at pH 9 with 50 mg C per L). Polyphosphate increased lead release by 540–4100%, likely due to aqueous complexation and possibly due to colloidal dispersion.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...