Constructing Cu2O/Bi2MoO6 p–n heterojunction towards boosted photo-assisted-electro-Fenton-like synergy degradation of ciprofloxacin†
Abstract
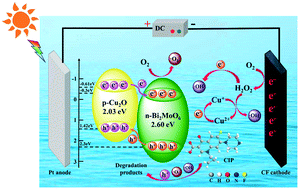
The long-term overuse of ciprofloxacin has resulted in its ubiquitous release into aquatic environments, seriously threatening public and ecological security. Herein, a photo-assisted-electro-Fenton-like (PAEF-like) system using p–n type Cu2O/Bi2MoO6 (CBM) as photoelectric catalyst was designed for efficient ciprofloxacin removal. The realization of photo-assisted function benefited from the perfectly constructed p–n heterojunction, which effectively regulated the carrier migration behaviors and drove the directional delivery of photoinduced electrons with flexible reactivity. Furthermore, photoinduced electrons directly or indirectly promoted the activation of H2O2 to enhance the ability of the PAEF-like synergy system to form ˙OH, improving the photoelectric catalytic activity. As dominant active species, ˙OH cooperated with h+ and ˙O2−, leading to the efficient elimination of ciprofloxacin. Finally, the degradation rate within 120 min reached almost 100%, and the corresponding kinetic constant was 208 and 1.5 times that of the photocatalytic and EF-like system, separately. Importantly, CBM-25% still maintained superior removal effect after four consecutive runs, revealing the high stability and practical feasibility of the PAEF-like system.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...