Fast Cr(vi) wastewater remediation on a BixOy/CdS heterostructure under simulated solar light induction†
Abstract
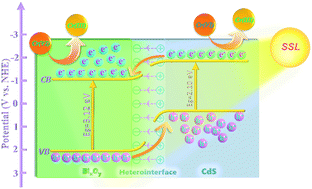
Bismuth oxide (BixOy), an important bismuth-based semiconductor with visible-light response, good structural stability and non-toxicity, has been identified as a potential candidate for chromium (Cr(VI))-containing wastewater remediation. However, the poor broadband light response and easy electron–hole recombination generally lead to unfavorable catalytic activity. Constructing a heterostructure is demonstrated to be an effective strategy for improving the catalytic performance of BixOy-based photocatalysts due to the improved photoresponse and promoted interfacial carrier mobility. Herein, CdS nanoparticles with low work function and good visible-light response were chosen as the cocatalyst to construct the p–n type BixOy/CdS heterostructure via a solvothermal method. Due to the formation of typical II-type induced mechanism, the interfacial carrier mobility and broadband light response were effectively improved; thereby, remarkably enhanced simulated solar-light (SSL)-induced aqueous Cr(VI) reduction activity (0.1265 min−1) was achieved by the optimum BixOy/CdS catalyst in the absence of scavengers, which is ∼34.2-fold greater than pristine BixOy (3.7 × 10−3 min−1) and possesses distinct advantage compared with previous reports. Also, the promoted carrier transfer effectively suppresses photocorrosion of the CdS microstructure, resulting in a desirable photostability under long-term photoinduction. This study provides a feasible strategy for aqueous Cr(VI) pollution remediation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...