Dual performing copper–platinum core–shell nanozyme for environmental electrochemistry–electrocatalytic oxidation and electroanalysis of ammonia†
Abstract
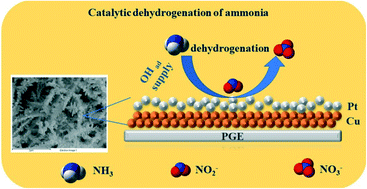
Platinum (Pt) is one of the most well-known catalytic/electrocatalytic materials for many important (electro)chemical conversion reactions. Their low availability and high cost limit their commercial applications. In the quest for alternative catalytic materials, core–shell nanostructures are evolving as a major alternative. Herein, we report a novel strategy for preparing copper–platinum core–shell nanostructures on a pencil graphite substrate (Cu@Pt/PGE), wherein copper nanostructures are prepared by template electrodeposition. This was followed by a galvanic replacement reaction for Pt modification. We show that the entire preparation could be completed in less than an hour at room temperature. The catalytic efficiency of the resulting dendritic Cu@Pt core–shell nanostructures is explored toward the ammonia oxidation reaction (AOR), since it is of great importance for environmental monitoring, ammonia removal and recently in ammonia fuel cells. Using the Cu@Pt/PGE nanozyme, the ammonia oxidation reaction could be carried out at −0.28 V vs. Ag/AgCl with promising catalytic performance, which is much higher than commercially available Pt disc electrodes. The catalyst could also be used for selective ammonia detection towards aquatic monitoring with a maximum sensitivity of 62 μA μM−1 cm−2 and a lower limit of detection of 613 nM. The results presented here may be highly useful for the development of next-generation alternative ammonia fuel cells and aquatic monitoring/purification as well as for the development of novel, high performance and affordable nanocatalytic systems.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanomaterial applications in water


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...