Extracellular interactions between graphene nanosheets and E-cadherin†
Abstract
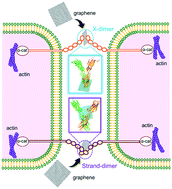
Nanoparticles (NPs), owing to their small size, are capable of crossing biological barriers to generate desired or unexpected effects. Previous studies considered the cell membrane as the primary interface of NP–cell interactions, while overlooking the complexity of the extracellular environment, where functional proteins are ubiquitous and potential targets for NPs prior to reaching the cell membrane surface. Here, by means of molecular dynamics (MD) simulation, we consider extracellular interactions between graphene nanosheets (GNs) and E-cadherin, which is a typical calcium-dependent adhesion protein maintaining the integrity of the intercellular junction via forming X- and strand-dimers. With the X-dimer interface identified to involve hydrophobic residue contacts plus salt bridges, our results demonstrate the reduction of the dimer stability by GNs through spontaneous intercalation into the dimer to disrupt the homophilic interactions. By contrast, the strand-dimer is maintained by docking of two Trp residues into pockets of opposing subunits with higher stability. GNs fail to enter the strand-dimer interface, but acquire adhesive contacts with the two subunits from opposite sides to tighten the dimer against mechanical separation, as evidenced by steered MD simulations. Oxidation and lipid adsorption are employed to represent the chemical and biological transformations of GNs, which are found to alleviate impacts through reduction of GN hydrophobicity plus surface passivation. These results can help explain the impairment of barrier integrity induced by NPs as observed in previous experiments, and highlight the importance of considering extracellular nano–bio interactions in future studies of nanomedicine and nano-safety evaluation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...