Degradation pathways of penthiopyrad by δ-MnO2 mediated processes: a combined density functional theory and experimental study†
Abstract
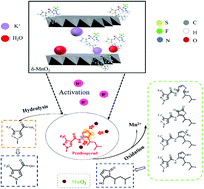
Penthiopyrad is a widely used succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor (SDHI) fungicide and frequently detected in natural environments. In order to better understand its fate in natural systems, the degradation of penthiopyrad by manganese dioxide (MnO2) was investigated in this study. The results show that penthiopyrad is rapidly degraded in the δ-MnO2 system. Moreover, density functional theory (DFT) calculations reveal that the atoms of C18, C12, and S1 in penthiopyrad have relatively high reactive active sites. The degradation products mainly include sulfoxides, sulfones, and diketone. A sulfoxide and sulfone are formed by the oxidation of the thioether group, and diketone is formed by the oxidation of the olefin group, respectively. Based on the DFT calculations and degradation products, the degradation pathway of penthiopyrad by MnO2 is proposed. This study also reveals that the degradation of penthiopyrad by δ-MnO2 is affected by various environmental factors. A warm environment, low pH, and co-existing humic acid are beneficial to the degradation of penthiopyrad in the δ-MnO2 system, whereas, co-existing metal cations inhibit penthiopyrad degradation. This result provides theoretical guidance for predicting the potential fate of penthiopyrad in natural environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...