Identifying sources of groundwater salinity and major hydrogeochemical processes in the Lower Kabul Basin aquifer, Afghanistan†
Abstract
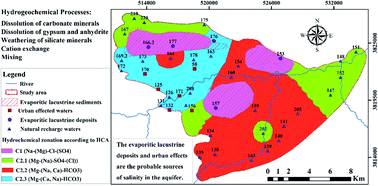
The Kabul Basin aquifer is the main source of water for domestic, agricultural and industrial use in Kabul city. Identifying the main hydrogeochemical processes and source of salinity is crucial for groundwater management. In this study, the results of 41 groundwater samples from the Lower Kabul Basin (LKB) aquifer were evaluated using major hydrogeochemical processes and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) methods. The electrical conductivity (EC) concentrations ranged from 672 to 15 290 μS cm−1 with a mean value of 1428 μS cm−1. The high spatial variations of EC in the LKB aquifer are due to different sources of salinity in groundwater. The results show that the Mg–(Ca, Na)–HCO3 water type is the dominant hydrogeochemical facies in the aquifer, followed by Mg–(Na)–Cl–(SO4), Na–(Mg)–SO4–(Cl), Na–Cl and Mg–Cl water types. The major factors controlling groundwater chemistry in the aquifer are the dissolution of carbonate, gypsum anhydrate minerals, weathering of silicates, ion exchange and mixing. Based on Cl/Br ratios, dissolution of minerals, anthropogenic and urban effects, and evaporitic lacustrine deposits are the possible sources of salinity in the aquifer. According to Cl/Br ratios and hierarchical cluster analysis, the evaporitic lacustrine deposits are the main source of salinity in the aquifer. The new groundwater survey also confirms the findings. The Cl/Br ratios and HCA successfully identified the sources of salinity in the LKB aquifer. The results of this study can provide a basis for local decision makers to develop effective and sustainable groundwater resources and environmental management strategies for Kabul city.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...