Oxygen vacancy engineered unsaturated coordination in cobalt carbonate hydroxide nanowires enables highly selective photocatalytic CO2 reduction†
Abstract
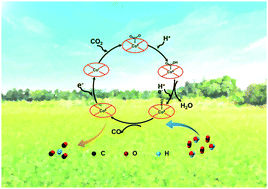
Cobalt carbonate hydroxide nanowires (Co(CO3)0.5(OH)·0.11H2O, CCO NWs) have gained significant attention as promising catalysts; however, their potential towards photocatalytic CO2 reduction (PCR) has not yet been explored. Herein, orthorhombic CCO NWs with rich oxygen vacancies (Vo-CCO NWs) have been manufactured by the self-photoetching approach under vacuum. Notably, the unsaturated coordinated cobalt centers, formed by destroying the interlayer carbonate ions bonded with Co species, act as the active sites, which can preferably adsorb and activate CO2 molecules, effectively inhibiting hydrogen evolution. Surprisingly, the Vo-CCO NWs manifest remarkable activity for CO2 reduction with a high CO evolution rate (1333.20 μmol h−1 g−1) and remarkable selectivity (98.2%) under visible light irradiation. Insightfully, a typical CoII/I reaction pathway can be demonstrated as the reduction mechanism supported by the combined evidence including in situ FTIR, CV, and in situ EPR results. This work provides a mild strategy for controllable oxygen vacancy generation on the surface of CCO, and also a deeper mechanistic study to understand the reaction process of PCR.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...