Visible and infrared optical modulation of PSLC smart films doped with ATO nanoparticles†
Abstract
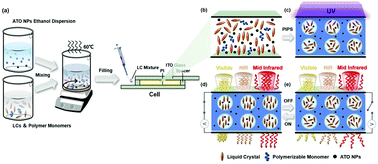
In recent years, smart windows have been gradually applied and developed in the fields of environmental protection, energy management, smart camouflage and display. With the continuous upgrading of market demand, smart windows with both visible and infrared band modulation functions are the future development trends. However, the optical modulation of smart windows is usually limited in the visible light band (380–780 nm). In this paper, we report a novel smart window by doping antimony doped tin oxide (ATO) nanoparticles (NPs) into polymer stabilized liquid crystal (PSLC) films. These films have the widest waveband modulation function among those reported so far, covering the visible and infrared regions (380–5500 nm). The transmittance of the as-prepared smart films can be changed reversibly from highly transparent (78.5%) state to a strong light scattering (10%) state in the visible region. In addition, due to the localized surface plasmon resonance of ATO NPs, up to 80.7% of the infrared invisible light can be effectively shielded. The significance of this research is to provide theoretical and technical support for the broadband optical modulation of novel smart windows.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...