Interface controlled solid-state lithium storage performance in free-standing bismuth nanosheets†
Abstract
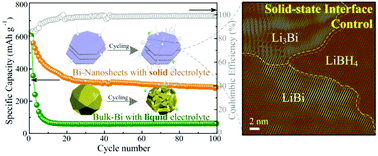
Bismuth (Bi) has recently been discovered as a potential lithium-ion anode material for batteries with high Li capacity and suitable equilibrium potential, and without dendrite formation. However, the reversible electrochemical stability remains insufficient for applications. Herein, it is demonstrated that two-dimensional free-standing Bi nanosheets (Bi-NSs) have superior anode performance using either liquid or solid electrolytes. The Bi-NSs with a uniform thickness of ∼40 nm prepared by aqueous methods exhibit a record high capacity of ∼287 mA h g−1 at a current density of 250 mA g−1 with the LiBH4 solid electrolyte even after 100 cycles. Fast and stable solid-state lithium plating and stripping occur without side reactions. The 2D layered nanostructure has more active sites and a shorter diffusion length, and forms stable interfaces with the electrolyte. The present work reveals a facile synthesis route of novel 2D materials and paves an efficient pathway for high-capacity and safe bismuth-based anodes for lithium batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...