Localization of metal ions in biomolecules by means of pulsed dipolar EPR spectroscopy
Abstract
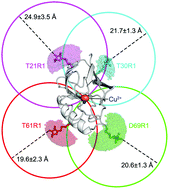
Metal ions are important for the folding, structure, and function of biomolecules. Thus, knowing where their binding sites are located in proteins or oligonucleotides is a critical objective. X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance are powerful methods in this respect, but both have their limitations. Here, a complementary method is highlighted in which paramagnetic metal ions are localized by means of trilateration using a combination of site-directed spin labeling and pulsed dipolar electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. The working principle, the requirements, and the limitations of the method are critically discussed. Several applications of the method are outlined and compared with each other.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 Frontier and Perspective articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...