The in situ growth of Cu2O with a honeycomb structure on a roughed graphite paper for the efficient electroreduction of CO2 to C2H4†
Abstract
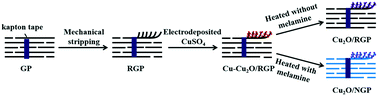
Metals and their alloy-based electrocatalysts continue to attract considerable attention for electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction reactions (CO2RRs). In this work, cuprous oxide (Cu2O) was supported on N-doped flexible roughed graphite paper (NGP) to fabricate Cu2O/NGP self-supporting electrocatalysts for CO2RRs by electrodeposition and heat treatment. In the Cu2O/NGP electrocatalyst, NGP acted as a current collector and conducting channel, which can effectively transfer electrons from the active sites of Cu2O to NGP, and thus, enhance the catalytic performance of Cu2O/NGP for CO2RRs. The overall Faradaic efficiency of Cu2O/NGP for CO2RRs reached 96% at −0.9 V vs. reversible hydrogen electrode, of which 35% originated from yielding ethylene (C2H4), suggesting its high activity and C2H4 selectivity. Furthermore, the excellent stability of Cu2O/NGP over 10 h made it preferable as an effective electrocatalyst for CO2RRs. The good electrocatalytic performance could be attributed to the unique self-supporting structure and the synergetic effect between Cu2O and NGP.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...