Effects of precipitants on the catalytic performance of Cu/CeO2 catalysts for the water–gas shift reaction
Abstract
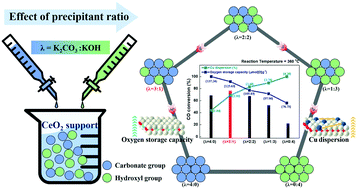
The water–gas shift (WGS) reaction has been attracting interest for on-site small-scale production of hydrogen. This study discusses the fabrication of inexpensive, high-performance Cu/CeO2 catalysts. To synthesize these catalysts, CeO2 supports were prepared using K2CO3/KOH as precipitants in different ratios. First, 20 wt% Cu was loaded onto the prepared CeO2 supports through incipient wetness impregnation. The ratios of the precipitants affect the physicochemical properties of the Cu/CeO2 catalysts, which in turn affects the catalytic performance. On increasing the K2CO3/KOH ratio, the surface area, oxygen storage capacity, and reducibility increased, while Cu dispersion decreased. To achieve high activity of Cu/CeO2 catalysts, the CeO2 support should be synthesized at the K2CO3 : KOH ratio of 3 : 1. This Cu/CeO2 catalyst exhibits the highest CO conversion between 200 and 400 °C, even at a very high gas hourly specific velocity of 50 102 h−1. This result shows that the catalytic performance is greatly influenced by various physicochemical properties such as surface area, oxygen storage capacity, Cu dispersion, and reducibility.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...