Coked Ni/Al2O3 from the catalytic reforming of volatiles from co-pyrolysis of lignin and polyethylene: preparation, identification and application as a potential adsorbent†
Abstract
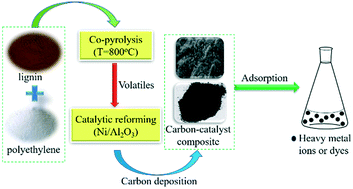
A novel and eco-friendly C–Ni/Al2O3 composite was prepared through Ni/Al2O3 coking during the catalytic reforming of volatiles from co-pyrolysis of lignin and polyethylene. The influence of Ni loading (0–20%) in the Ni/Al2O3 catalyst and catalytic reforming temperature (500–800 °C) on the characteristics of the C–Ni/Al2O3 composite was investigated, involving the analysis of SEM, XRD, TPO and FTIR. Fibrous carbon on the C–Ni/Al2O3 composite was produced by the catalyst Ni(10%)/Al2O3 at reforming temperatures of 600 and 700 °C, which was oxidized at around 500 °C according to the TPO analysis. The maximum deposition of carbon in the C–Ni(10%)/Al2O3 composite was about 10.86%, achieved at a catalytic reforming temperature of 700 °C. Abundant oxygen-containing functional groups were observed on the C–Ni/Al2O3 composite through the FTIR analysis, leading to the outstanding adsorption performance for pollutant removal from aqueous systems. The optimal C–Ni/Al2O3 composite was selected to investigate the effect of process conditions on the adsorption performance for Pb(II), Cr(VI), rhodamine B (RhB) and methyl orange (MO). The adsorption isotherms for the four mentioned pollutants were well fitted by the Langmuir model and the maximum adsorption amount for Pb(II), Cr(VI), RhB and MO was estimated to be 223.52, 54.90, 290.76 and 95.71 mg g−1, respectively. The results indicated that the as-prepared C–Ni/Al2O3 composite had potential for the removal of heavy metal ions and hazardous organic compounds from aqueous systems.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging Investigator Series


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...