The application and improvement of TiO2 (titanate) based nanomaterials for the photoelectrochemical conversion of CO2 and N2 into useful products
Abstract
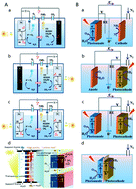
In this review, we describe the photoelectrochemical (PEC) transformation of atmospheric species such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrogen (N2) into useful industrial products on TiO2 and TiO2 composite photoelectrodes. The configuration and classification of PEC cells, and the mechanisms for PEC CO2 and N2 reduction are discussed in detail. Although CO2 and N2 PEC reduction processes are similar to each other with regards to electrode materials, basic working principle and the configuration of the reaction systems, their mechanisms differ significantly. Therefore, various examples of the PEC reduction of CO2 and N2 at TiO2 and titanate-based semiconductor photoelectrodes with different specific cell constructions and reaction mechanisms are introduced and discussed. Despite the significant progress on the PEC reduction of CO2 and N2 at TiO2 based electrodes, some challenges still remain and are outlined. In addition, we propose new approaches to further improve the PEC properties of TiO2 and titanate-based semiconductors for the selective reduction of CO2 and N2 into useful products.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...