Recent discoveries in the reaction mechanism of heterogeneous electrocatalytic nitrate reduction
Abstract
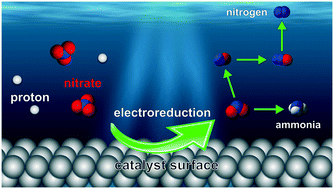
The importance of maintaining a balanced nitrogen cycle and rectifying the accumulation of nitrate in water streams creates a need for technologies that can convert nitrate species. Heterogeneous electrocatalytic nitrate reduction (NO3RR) is a promising technology because it can use renewable electricity to convert nitrate to nitrogen or ammonia without chemical reductants, hydrogen gas, or the production of biological waste. This review discusses the fundamental mechanism of nitrate reduction by exploring the rate-determining conversion of nitrate to nitrite and NO, and the selectivity pathways that lead to ammonia, nitrogen gas, and nitrogen oxides. Additionally, it explores several important techniques for evaluating nitrate reduction electrocatalysts, including methods to quantify the electrochemically active surface area and the product selectivity. This review highlights the activity and selectivity trends for electrocatalysts which include metals, alloys, and more recent work on sulfides, oxysulfides, oxides, phosphides, and N-doped materials. Factors that influence the reactivity and selectivity trends, such as adsorption energy of the intermediates, reaction conditions, and surface contaminants are also discussed. Overall, this review shows how mechanistic studies have led to a better understanding of NO3RR. Targeted and controlled NO3RR studies can lead to better synergy between experimental and computational results, predictive mechanistic understanding, and discovery of new NO3RR electrocatalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...