A CuMn2O4 spinel oxide as a superior catalyst for the aerobic oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural toward 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid in aqueous solvent†
Abstract
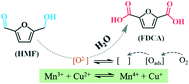
A CuMn2O4 spinel oxide was prepared via a freezing-assisted sol–gel method and used in the aerobic oxidation of 5-hydroxylmethylfurfural (HMF) toward 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA) in aqueous solvent. A highest FDCA yield of 92.1% over the CuMn2O4 spinel oxide was achieved and the catalyst could be regenerated by calcination in air after the sixth consecutive run, outperforming several other Mn-based spinel and single oxide catalysts. Kinetic studies reveal that HMF → 2,5-diformylfuran → 5-formylfuran-2-carboxylic acid (FFCA) → FDCA is the primary reaction route of the reaction and that the oxidation of FFCA is the rate-determining step over the CuMn2O4 spinel. Characterization measurements show that Mn species enrichment and proper Mn4+/Mn3+, Cu2+/Cu+ and Cu/Mn ratios on the surface of the catalyst led to an appropriate Olatt./Oads. ratio, which facilitated oxygen mobility between the Olatt. consumption and the Olatt. generation via the refilling of oxygen vacancies. Synergistic effects between Mn and Cu in the CuMn2O4 spinel inhibit the secondary reaction and accelerate the rate-determining step rate to enhance FDCA formation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...