Intense chiral signal from α-helical poly-l-alanine observed in low-frequency Raman optical activity†
Abstract
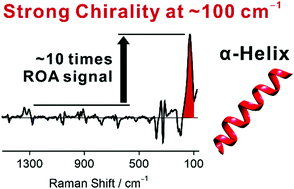
Raman optical activity (ROA) spectral features reliably indicate the structure of peptides and proteins, but the signal is often weak. However, we observed significantly enhanced low-frequency bands for α-helical poly-L-alanine (PLA) in solution. The biggest ROA signal at ∼100 cm−1 is about 10 times stronger than higher-frequency bands described previously, which facilitates the detection. The low-frequency bands of PLA were compared to those of α-helical proteins. For PLA, density functional simulations well reproduced the experimental spectra and revealed that about 12 alanine residues within two turns of the α-helix generate the strong ROA band. Averaging based on molecular dynamics (MD) provided an even more realistic spectrum compared to the static model. The low-frequency bands could be largely related to a collective motion of the α-helical backbone, partially modulated by the solvent. Helical and intermolecular vibrational coordinates have been introduced and the helical unwinding modes were assigned to the strongest ROA signal at 101–128 cm−1. Further analysis indicated that the helically arranged amide and methyl groups are important for the strong chiral signal of PLA, while the local chiral centers CαH contribute in a minor way only. The strong low-frequency ROA can thus provide precious information about the motions of the peptide backbone and facilitate future protein studies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...