Molecular dynamics study on the inhibition mechanisms of ReACp53 peptide for p53–R175H mutant aggregation†
Abstract
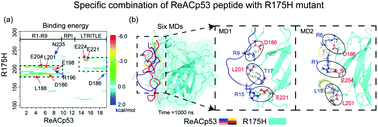
p53 mutant aggregation can lead to loss-of-function (LoF), dominant-negative (DN) and gain-of-function (GoF) effects, involving in tumor growth. Finding inhibition methods of p53 mutant aggregation is a key step for developing new therapeutics against aggregation-associated cancers. Recent studies have shown that a cell-permeable peptide, ReACp53, can inhibit aggregation of the p53 mutant and restore p53 nuclear function as a transcriptional factor, showing extraordinary therapeutic potential. However, the molecular mechanism underlying the inhibition of p53 mutant aggregation by the ReAp53 peptide is unclear. In this work, we used all-atom molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to investigate the effect of ReACp53 peptide on the structural and dynamic properties of the p53 core domain (p53C) of the aggregation-prone R175H mutant. Our simulations revealed that the ReACp53 peptide can stabilize the ordered secondary structure and decrease the flexibility of disordered loops of the R175H mutant through increasing the intra-interactions of p53C. Moreover, we found that ReACp53 peptide specifically binds to the fragment (residues 180–233) of the R175H mutant through strong hydrophobic interactions with residues L188 and L201 and a salt bridge or hydrogen bond formation with residues D186, E198, D204, E221 and E224. The specific binding pattern protects the aggregation-prone fragment (residues 182–213) from exposure to water. Hence, we suggested that the ReACp53 peptide inhibits aggregation of the R175H mutant by restoring the wild-type conformation from an aggregation-prone state and reducing the exposure of the aggregation-prone segment. These results provide molecular mechanistic insight into inhibition of the ReACp53 peptide on amyloid aggregation of the R175H mutant.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...