Antiviral drug design based on the opening mechanism of spike glycoprotein in SARS-CoV-2†
Abstract
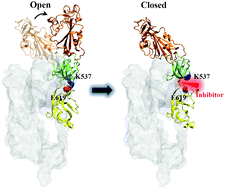
The novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) enters the host cell after the receptor binding domain (RBD) of the virus spike (S) glycoprotein binds to the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2). This binding requires the RBD to undergo a conformational change from a closed to an open state. In the present study, a key pair of salt bridges formed by the side chains of K537 and E619, residues at the interfaces of SD1 and SD2, respectively, was identified to promote the opening of the RBD. Mutations of K537Q and E619D reduced their side chain lengths and eliminated this pair of salt bridges; as a result, the opening of the RBD was not observed in the MD simulations. Thus, blocking the formation of this pair of salt bridges is a promising approach for treating novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). FDA approved drug molecules were screened by their capabilities of blocking the formation of the key pair of salt bridges, achieved by their positional stabilities in the cavity containing the side chains of K537 and E619 formed in the interface between SD1 and SD2. Simeprevir, imatinib, and naldemedine were identified to possess the desired capability with the most favorable interaction energies.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...