Reaction mechanism of atomic layer deposition of aluminum sulfide using trimethylaluminum and hydrogen sulfide†
Abstract
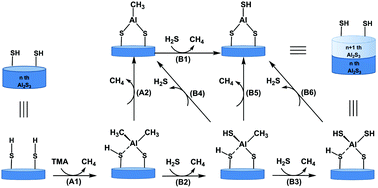
Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is a nanopreparation technique for materials and is widely used in the fields of microelectronics, energy and catalysis. ALD methods for metal sulfides, such as Al2S3 and Li2S, have been developed for lithium-ion batteries and solid-state electrolytes. In this work, using density functional theory calculations, the possible reaction pathways of the ALD of Al2S3 using trimethylaluminum (TMA) and H2S were investigated at the M06-2X/6-311G(d, p) level. Al2S3 ALD can be divided into two consecutive and complementary half-reactions involving TMA and H2S, respectively. In the TMA half-reaction, the methyl group can be eliminated through the reaction with the sulfhydryl group on the surface. This process is a ligand exchange reaction between the methyl and sulfhydryl groups via a four-membered ring transition state. TMA half-reaction with the sulfhydrylated surface is more difficult than that with the hydroxylated surface. When the temperature increases, the reaction requires more energy, owing to the contribution of the entropy. In the H2S half-reaction, the methyl group on the surface can further react with the H2S precursor via a four-membered ring transition state. The orientation of H2S and more molecules have minimal effect on the H2S half-reaction. The reaction involving H2S through a six-membered ring transition state is unfavorable. In addition, the methyl and sulfhydryl groups on the surface can both react with the adjacent sulfhydryl group on the subsurface to form and release CH4 or H2S in the two half-reactions. Furthermore, sulfhydryl elimination occurs more easily than methyl elimination on the surface. These findings for the TMA and H2S half-reactions of Al2S3 ALD may be used for studying precursor chemistry and improvements in the preparation of other metal sulfides for emerging applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...