The effects of substitutional doping on Cu vacancy formation in Cu2O(111): a density functional theory study
Abstract
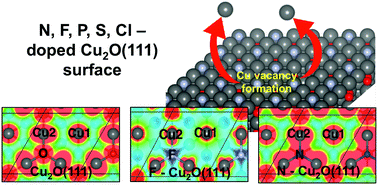
Using density functional theory (DFT) calculations, we examined the effects of substitutional doping on the formation of Cu vacancies in Cu2O(111). Upon replacing coordinatively unsaturated O with other elements (N, F, P, S, and Cl) and calculating the formation energies, we found that compared to the undoped surface, Cu vacancy formation is most favorable in the F-doped surface and least favorable in the N-doped Cu2O(111) surface. In addition, we found that in most cases, vacancy formation of the coordinatively saturated Cu has higher vacancy formation energy than coordinatively unsaturated Cu atoms. In the electron localization function plots and the projected charge distributions of the local density of states, we found bonding enhancement between Cu and N in N-Cu2O(111) but no corresponding enhancement was observed in the F-doped surface. Our results showed that the interaction between the substitutional dopants and the Cu atoms affects the formation of the doped system and the Cu vacancy formation in the surface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...