Conformation-specific perturbation of membrane dynamics by structurally distinct oligomers of Alzheimer's amyloid-β peptide†
Abstract
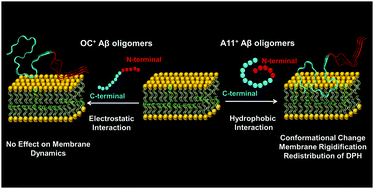
The accumulation of toxic soluble oligomers of the amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) is a key step in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. There are mainly two conformationally distinct oligomers, namely, prefibrillar and fibrillar oligomers, that are recognized by conformation-specific antibodies, anti-amyloid oligomer antibody (A11) and anti-amyloid fibrillar antibody (OC), respectively. Previous studies have shown that the interaction of Aβ oligomers with the lipid membrane is one of the key mechanisms of toxicity produced by Aβ oligomers. However, the mechanism by which structurally distinct Aβ oligomers interact with the lipid membrane remains elusive. In this work, we dissect the molecular mechanism underlying the interaction of structurally distinct Aβ42 oligomers with the lipid membrane derived from the brain total lipid extract. Using picosecond time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy, we show that the A11-positive Aβ42 oligomers undergo a membrane-induced conformational change that promotes the deeper immersion of these oligomers into the lipid hydrocarbon region and results in an increase in the membrane micro-viscosity. In sharp contrast, OC-positive Aβ42 oligomers interact with the lipid membrane via electrostatic interactions between the negatively-charged lipid headgroup and positively-charged residues of Aβ42 without perturbing the membrane dynamics. We show that the two structurally distinct Aβ42 oligomers demonstrating different interaction mechanisms with the lipid membrane eventually lead to the formation of typical amyloid fibrils. Our findings provide the mechanistic underpinning of the perturbation of lipid membranes by two conformationally distinct Aβ42 oligomers and can be of prime importance in designing anti-Alzheimer's therapeutic agents targeting Aβ-membrane interactions.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...