Electrochemical characterization and thermodynamic analysis of TEMPO derivatives in ionic liquids†
Abstract
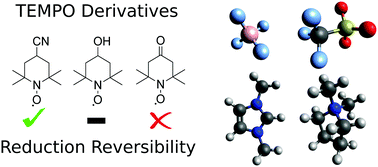
In this study we investigate the reversibility of the reduction process of three TEMPO derivatives – TEMPOL, 4-cyano-TEMPO, and 4-oxo-TEMPO. The [C2mim][BF4] and [C4mpyr][OTf] ionic liquids (ILs) were used to perform cyclic voltammetry (CV) to analyse the redox potentials of the TEMPO derivatives. The former was previously shown to quench the aminoxy anion of TEMPO through a proton transfer reaction with the cation, whereas the latter supported the irreversibility of the TEMPO reduction process. In CV results on TEMPO derivatives, it was shown that [C4mpyr][OTf] could allow for a high degree of reversibility in the reduction of 4-cyano-TEMPO and a moderate degree of reversibility in the reduction of TEMPOL. In comparison, reduction of 4-cyano-TEMPO was predominantly irreversible in [C2mim][BF4], whilst TEMPOL showed complete irreversibility. 4-Oxo-TEMPO did not show any notable reduction reversibility in either IL tested. Reduction potentials showed little variation between the derivatives and 0.2 V variation between the ILs, with the most negative reduction potential being observed at −1.43 V vs. Fc/Fc+ for TEMPOL in [C4mpyr][OTf]. To explain the varying degrees of reversibility of the reduction process, four types of side reactions involving proton transfer to the aminoxy anion were studied using highly correlated quantum chemical methods. Proton transfer from the IL cation was shown to have the ability to quench all three aminoxy anions depending on the IL used. On average, TEMPOL was shown to be the most susceptible to proton transfer from the IL cation, having an average Gibbs free energy (GFE) of 10.5 kJ mol−1 more negative than that of 4-cyano-TEMPO, which was shown to have the highest GFE of proton transfer. Side reactions between water and aminoxy anions were also seen to have the potential to contribute to degradation of the aminoxy anions tested, with 4-oxo-TEMPO being shown to be the most reactive to degradation with water with a GFE of −12.6 kJ mol−1. 4-Oxo-TEMPO was found to be highly susceptible to self-quenching by its aminoxy anion and radical form with highly negative proton transfer GFEs of −47.9 kJ mol−1 and −57.7 kJ mol−1, respectively. Overall, 4-cyano-TEMPO is recommended as being the most stable of the aminoxy anions tested with TEMPOL, thus providing a viable alternative to improve solubility should the IL be tuned to maximize its stability.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...