Luminescence properties and energy transfer of La3Ga5SiO14:Eu3+, Tb3+ phosphors
Abstract
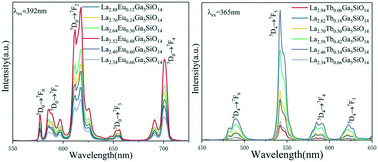
In this paper, a series of Eu3+/Tb3+ doped La3Ga5SiO14 (LGS:Eu3+, Tb3+) phosphors with excellent performance have been synthesized by high-temperature solid-phase method. The effects of Eu3+ and Tb3+ doping in LGS on the host lattice were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) proved that the Eu3+ and Tb3+ ions were successfully doped into the LGS host. The doped Eu3+/Tb3+ ions only occupy the eight-coordinated La3+ sites. The concentration quenching points of LGS:Eu3+ and LGS:Tb3+ phosphors were determined to be 0.16 and 0.18, respectively. The luminescence performance and fluorescence lifetime of LGS:Eu3+, Tb3+ were studied. LGS:Eu3+, Tb3+ phosphors successfully realized Tb3+ → Eu3+ energy transfer to enhance Eu3+ luminescence. The energy transfer mechanism is speculated on using the experimental results. The energy transfer efficiency from Tb3+ to Eu3+ is about 66.83% in La2.46Tb0.18Eu0.36Ga5SiO14. The LGS:Eu3+, Tb3+ phosphors can achieve tunable luminescence by controlling the doping concentrations of Eu3+ and Tb3+. The ΔE is calculated to be 0.2567 eV for the La2.70Eu0.12Tb0.18Ga5SiO14 phosphor.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanomaterials


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...