Azacalixphyrins as an innovative alternative for the free-radical photopolymerization under visible and NIR irradiation without the need of co-initiators†
Abstract
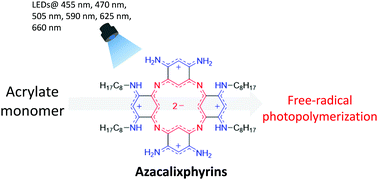
Azacalixphyrins are unique aromatic macrocycles featuring strong absorption from the visible to the near-infrared (NIR) spectral ranges. This work demonstrates through EPR spin-trapping experiments that the N-alkyl tetrasubstituted azacalixphyrin (ACP) can lead to the formation of carbon-centered radicals initiating for the free-radical photopolymerization (FRP) of bio-based acrylate monomer upon the irradiation of several light emitting diodes, which emissions range from 455 to 660 nm. Compared to other previously reported systems, the tremendous advantage of the ACP photoinitiating system is its ability to promote photopolymerization on its own, avoiding the introduction of co-initiators. A new potential application of this promising photoinitiator is highlighted through the fabrication of well-defined microstructures under NIR laser diode irradiation at λ = 800 nm.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...