Cascade communication in disordered networks of enzyme-loaded microdroplets†
Abstract
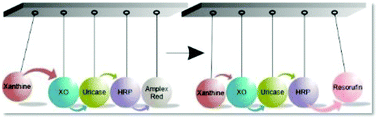
A network of aqueous emulsion droplets that exhibits programmed and directional chemical inter-droplet communication is described. A non-reciprocal transfer of substrates between enzyme-containing aqueous emulsion droplets is realized by (biochemically) induced osmolarity gradients and concomitant concentration gradients are used to direct a multistep enzymatic cascade reaction across multiple droplets.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...