Electrochemically captured Zintl cluster-induced bismuthene for sodium-ion storage†
Abstract
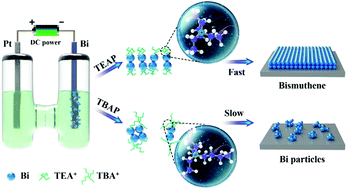
Bismuthene was prepared via the oxidation of Zintl clusters by electrochemical cathodic corrosion. It was found that the conversion of Zintl clusters from Bi22− to Bi2 occurred in the electrolyte having short alkyl chains due to the faster kinetics of highly reactive carbocation. Considering that c-Na3Bi exists in a wide voltage range, monitored by in situ XRD, a new wide peak for the as-obtained bismuthene in the CV curve was noticed, which benefits the improvement of electrochemical performances.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...