Ultrasensitive detection of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) in whole blood using dispersible electrodes†
Abstract
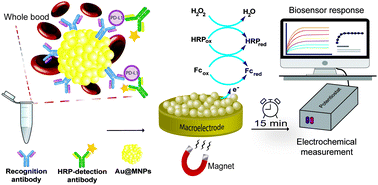
The direct quantification of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) as a biomarker for cancer diagnosis, prognosis and treatment efficacy is an unmet clinical need. Herein, we demonstrate the first report of rapid, ultrasensitive and selective electrochemical detection of PD-L1 directly in undiluted whole blood using modified gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles as “dispersible electrodes” with an ultralow detection limit of 15 attomolar and a response time of only 15 minutes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...