Glutathione-degradable polydopamine nanoparticles as a versatile platform for fabrication of advanced photosensitisers for anticancer therapy†
Abstract
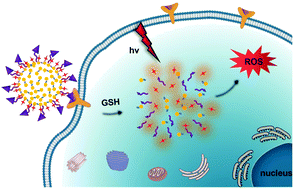
A series of glutathione (GSH)-responsive polydopamine (PDA) nanoparticles (NPs) were prepared using a disulfide-linked dopamine dimer as starting material, of which the size could be tuned systematically by adjusting the amount of ammonia solution used. Molecules of a phthalocyanine (Pc)-based photosensitiser and an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeting peptide were then sequentially immobilised on the surface of the NPs through coupling with the surface functionalities of PDA. The immobilised Pc molecules in the resulting nanosystem were photodynamically inactive due to the strong self-quenching effect and the quenching by the PDA core. Upon exposure to GSH in phosphate-buffered saline or EGFR-positive cancer cells, namely A549 and A431 cells, the NPs were disassembled through cleavage of the disulfide linkages to release the Pc molecules, thereby restoring their fluorescence emission and singlet oxygen generation. The NPs with the smallest size (ca. 200 nm in diameter) exhibited the highest cellular uptake and high photocytotoxicity with IC50 values as low as 0.05 μM based on Pc. These NPs could also accumulate and be activated in the tumour of A431 tumour-bearing nude mice, lighting up the tumour with fluorescence over a period of 72 h and completely eradicating the tumour through laser irradiation for 10 min (675 nm, 20 J cm−2). The results suggest that these biodegradable and versatile PDA-based NPs can serve as a promising nanoplatform for fabrication of advanced photosensitisers for targeted photodynamic therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...