Hydrophilic hindering and hydrophobic growing: a vesicle glycometabolism multi-drug combination therapeutic against Alzheimer's disease†
Abstract
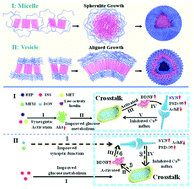
Advanced drug vehicle exploitation and the sophisticated synergy mechanism revelation are two great difficulties in combination therapy. Compared with most readily available polymer micelles, some undiscovered complex chemical design principles limit the expanding research of polymer vesicles. Here, polycaprolactone (PCL)-g-Dextran vesicle that dextran brush steric hindrance guide PCL lamellae-aligned growth was synthesized. The effect of the glycometabolism multi-drug vesicle combination treatment and synergism mechanism were investigated on senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 (SAMP8) mice. The main insulin sensitizer drug could improve the memory ability of mice to a small extent, and the main insulin secretion promoter drug had little beneficial effect. Moreover, the triple anti-insulin resistant drugs of insulin (INS), repaglinide (REP) and metformin hydrochloride (MET) activated the glycometabolism-related bio-signals, and the energy cycle was normalized successfully. The insulin intracellular uptake and utilization efficiency could be the reason for the gap. The upregulation of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protein confirmed that the crosstalk between the mitochondria and synapse contributes to the nerve repair. This study provided an excellent drug combination vesicle to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD). The discovery of the combination mechanism leads to an improvement in the AD clinical treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...