Plasmonic enhanced enzyme activity by catalytic cascade induced mutual benefit tumor starvation/immune/photothermal therapy†
Abstract
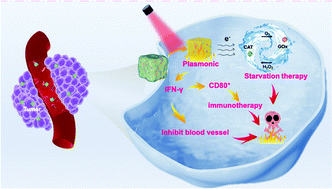
Single tumor starvation therapy can activate other signaling pathways in tumor cells and easily induce tumor cell metastasis. This research proposes an intelligent nanoparticle, which is effectively combined with plasmonic and immunotherapy to realize a new strategy of “upstream consumption and downstream blocking” of nutrients in tumor sites. The intelligent nanoparticle (Ag-G/C@M) was composed of Ag NCs loaded with glucose oxidase (GOx), catalase (CAT) and coated with the tumor cytomembrane (M). Homologous targeting of tumor cytomembrane facilitated more delivery of Ag-G/C@M to tumor sites and then the plasmonic excited from Ag-G/C@M can increase the catalytic efficiency of the enzymatic reaction. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) produced by Ag-G/C@M through the consumption of glucose is further catalyzed by CAT to produce oxygen (O2). This self-reinforcing cascade reaction not only consumes the nutrients of tumor cells, but also the plasmonic-induced photothermal therapy can further stimulate the immune system to produce interferon-γ (IFN-γ), blocking angiogenesis and restricting the nutrient supply of tumor cells. This strategy takes the nutrition necessary for cell survival as the entry point, through endogenous continuous consumption of intracellular nutrients and containment of exogenous supplementation, combined with plasmonic thermal effect and immunotherapy to kill tumor cells, which provides a new way of treating cancer safely and effectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...