Visualization of USPIO-labeled melt-electrowritten scaffolds by non-invasive magnetic resonance imaging†
Abstract
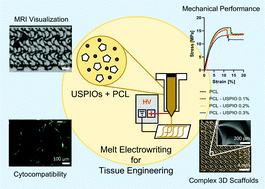
Melt electrowriting (MEW) is a high-resolution fiber-forming technology for the digital fabrication of complex micro-structured scaffolds for tissue engineering, which has convincingly shown its potential in in vitro and in vivo animal studies. The clinical translation of such constructs to the patient requires the capability to visualize them upon implantation with clinically accepted methods such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). To this end, this work presents the modification of polycaprolactone (PCL) scaffolds with ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide (USPIO) nanoparticles to render them visualizable by MRI. Composite scaffolds containing up to 0.3 weight % USPIOs were 3D printed by MEW and could be sensitively detected in vitro using T2- and T2*-weighted MRI. At the same time, USPIO incorporation did not affect the usability of PCL for tissue engineering applications as demonstrated by the mechanical and cytocompatibility evaluation. Concentrations up to 0.2% caused small to no decrease in the ultimate tensile strength and Young's modulus. Cytocompatibility tests resulted in excellent cell viability, with proliferating cells adhering to all the scaffolds. This work contributes to the materials library for MEW and opens the possibility of using MRI for longitudinal monitoring of MEW grafts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...