Electrochemical sandwich-type immunosensor for the detection of PSA based on a trimetallic AgAuPt nanocomposite synthesized using the galvanic replacement reaction†
Abstract
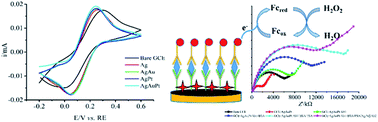
A sandwich-type electrochemical immunoassay was introduced for the determination of the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) biomarker. A direct and simple galvanic replacement reaction was performed between the Ag framework and metallic salts of tetrachloroauric(III) acid trihydrate and chloroplatinic acid to produce a trimetallic composite of AgAuPt. The trimetallic composite of AgAuPt was applied to the preparation of the capture layer of the immunoassay for stabilizing the primary Ab at the surface of the prepared composite. The immunoassay detection layer was also prepared using a labeled antibody containing a bimetallic composite of AgPt as a label. The various procedures in the immunoassay fabrication were monitored step by step using cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Also, the electrochemical determination of PSA was performed using differential pulse voltammetry in the presence of the ferrocene redox probe and H2O2. Furthermore, the effective parameters in the fabrication of the immunoassay included the drop volume of the AgAuPt trimetallic composite and the incubation time for the immobilization of biomolecules (i.e., Ab1, BSA, PSA, and labeled Ab2), and the concentration of H2O2 were optimized during the determination of PSA. Then, the determination of PSA was performed under optimized conditions. It could be seen that there was a linear relation between the PSA concentration and DPV responses in the concentration range of 50 pg mL−1 to 500 ng mL−1 and the limit of detection (LOD) for the proposed immunoassay was calculated as 17.0 pg mL−1. In the following investigation, the cross-reactivity of the proposed immunoassay was studied in the presence of BSA, CEA, IgG, and human hepatitis surface antigen, in which the results showed a negligible change in the performance of the immunoassay.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...