Regularities of element migration based on rock spectral features: a case study of the Liwu copper deposit
Abstract
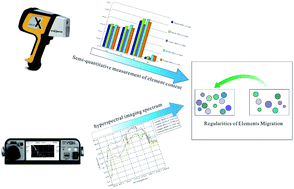
The Liwu copper–zinc mining area has a complex topographical environment. Using traditional prospecting methods, it is difficult and costly to carry out traditional prospecting research on a large scale. This study used portable X-ray fluorescence (pXRF) spectrometry and hyperspectral imaging for analysing rock samples in the B2 ore body of the Liwu copper–zinc deposit. The hyperspectral imaging data and the measured indoor spectral characteristic curve of the same lithological rock have a certain similarity. The absorption or reflection characteristics in the same waveband were similar. The main elements were Cu and Zn in the ore body, Pb which was obviously brought out, and Cd, Sn and Sb which were brought in. It is believed that the mass migration of Cd, Sn, Sb and Pb elements plays an important role in the precipitation and enrichment of Cu and Zn elements. This method can be used to quickly determine element migration. The combination of the two analytical methods of pXRF and hyperspectral analysis, the low requirements of the work site and the fast and efficient characteristics, mean this method has unique advantages in analysing and monitoring environmental pollution, rock and mineral analysing and prospecting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...