De novo structural determination of oligosaccharide isomers in glycosphingolipids using logically derived sequence tandem mass spectrometry†
Abstract
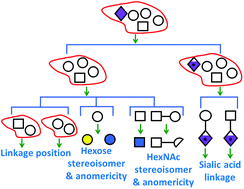
Despite the importance of carbohydrates in biological systems, structural determination of carbohydrates remains difficult because of the large number of isomers. In this study, a new mass spectrometry method, namely logically derived sequence tandem mass spectrometry (LODES/MSn), was developed to characterize oligosaccharide structures. In this approach, sequential collision-induced dissociation (CID) of oligosaccharides is performed in an ion trap mass spectrometer to identify the linkage position, anomeric configuration, and stereoisomers of each monosaccharide in the oligosaccharides. The CID sequences are derived from carbohydrate dissociation mechanisms. LODES/MSn does not require oligosaccharide standards or the prior knowledge of the rules and principles of biosynthetic pathways; thus LODES/MSn is particularly useful for the investigation of undiscovered oligosaccharides. We demonstrated that the structure of core oligosaccharides in glycosphingolipids can be identified from more than 500 000 isomers using LODES/MSn. The same method can be applied for determining the structures of other oligosaccharides, such as N-, and O-glycans, and free oligosaccharides in milk.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...