Detection of acquired radioresistance in breast cancer cell lines using Raman spectroscopy and machine learning†
Abstract
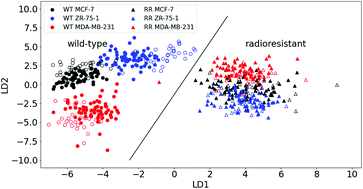
Radioresistance—a living cell's response to, and development of resistance to ionising radiation—can lead to radiotherapy failure and/or tumour recurrence. We used Raman spectroscopy and machine learning to characterise biochemical changes that occur in acquired radioresistance for breast cancer cells. We were able to distinguish between wild-type and acquired radioresistant cells by changes in chemical composition using Raman spectroscopy and machine learning with 100% accuracy. In studying both hormone receptor positive and negative cells, we found similar changes in chemical composition that occur with the development of acquired radioresistance; these radioresistant cells contained less lipids and proteins compared to their parental counterparts. As well as characterising acquired radioresistance in vitro, this approach has the potential to be translated into a clinical setting, to look for Raman signals of radioresistance in tumours or biopsies; that would lead to tailored clinical treatments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...