Protein-templated gold nanoclusters as specific bio-imaging probes for the detection of Hg(ii) ions in in vivo and in vitro systems: discriminating between MDA-MB-231 and MCF10A cells†
Abstract
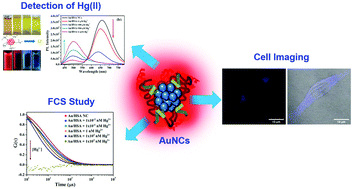
Gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) synthesized within a protein (Human Serum Albumin, HSA) template exhibited intense red luminescence accompanied by a quantum yield >10% and remarkable photo and cluster-core stability for a prolonged period (more than a year). These photoluminescent nanoclusters (NCs) were resistant to chemical and thermal perturbations but break down selectively and highly sensitively in the presence of mercury, Hg(II), ions. The AuNCs were efficient in quantifying Hg(II) ions in solution as well as bound to the hormone insulin. By exploiting the auto-fluorescence of these AuNCs, we demonstrated that our AuNCs were able to sense Hg(II) ions at single-molecule sensitivity using Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy (FCS), highlighting a detection limit in the sub-nanomolar regime. The translational diffusion time of the AuNCs decreased significantly upon the interaction with Hg(II) ions and resulted in the formation of smaller sized clusters. A cell viability study reveals the non-toxic nature of these nano-probes, which thus can be used for cell imaging. Interestingly, a cell line-based study reveals that the fluorescence intensity of AuNCs could be detected in cancerous MDA-MB-231 cells but not in non-cancerous breast-derived MCF10A cells. Further, time lapse fixed cell imaging by confocal microscopy revealed that the fluorescence of AuNCs could be quenched by Hg(II) ions inside the MDA-MB-231 cells. Thus the objective of our study is to appraise the sensitive in vivo as well as in vitro detection of Hg(II) ions using AuNCs as a probe.
- This article is part of the themed collection: #RSCPoster Conference


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...